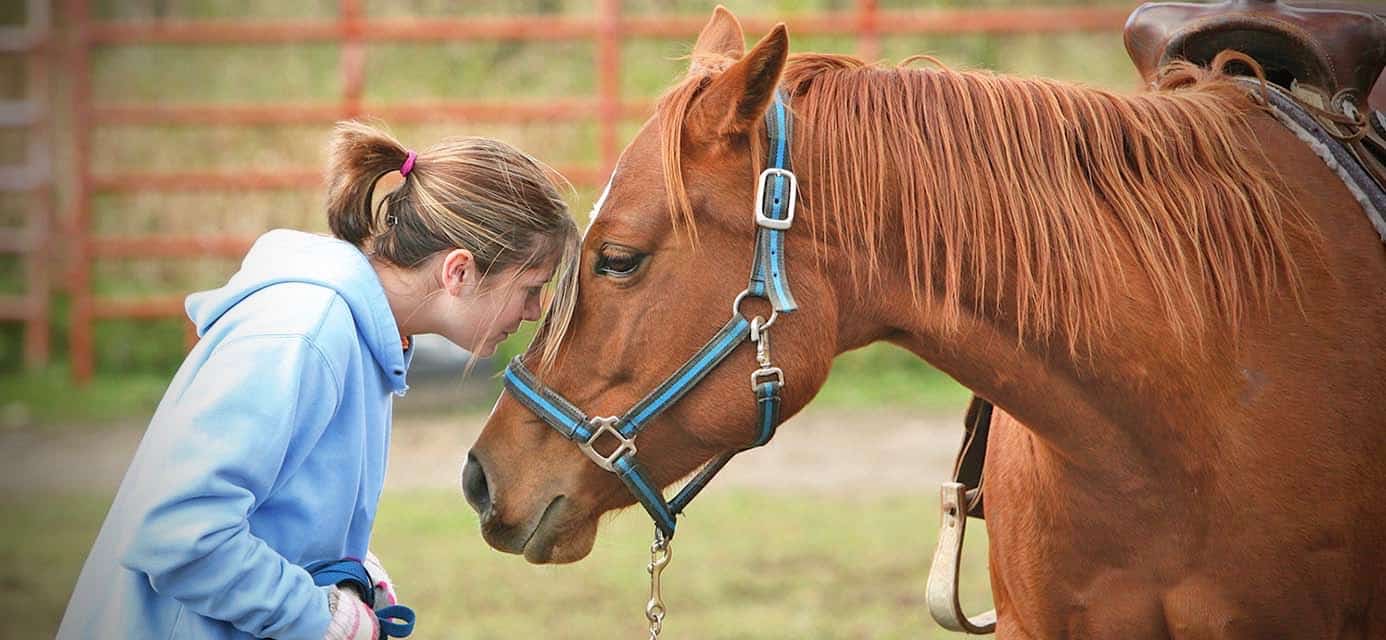
Have you ever wondered what makes horseback riding such a unique and rewarding experience? Well, let me tell you, horseback riding goes beyond just the thrill of being on a horse. In fact, did you know that horseback riding is closely connected to a form of therapy known as animal-assisted therapy? In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of horseback riding and its connection to animal-assisted therapy. You’ll learn how riding a horse can have a positive impact on mental, emotional, and even physical well-being. So, if you’re interested in learning more about this incredible connection, keep reading!
Horseback riding is not just about sitting on a horse and enjoying the ride. It’s about forming a unique bond with these magnificent animals and experiencing the therapeutic benefits they can offer. Whether you’re someone who has physical disabilities, mental health challenges, or simply looking for a way to de-stress and connect with nature, horseback riding can be a powerful tool. In animal-assisted therapy, horses are used as a means of therapy to help individuals overcome various obstacles and improve their overall well-being. The rhythmic motion of riding a horse can provide physical benefits such as improved balance, coordination, and muscle strength. Additionally, interacting with horses has been shown to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression, as well as promote socialization and emotional healing. So, if you’re curious to learn more about the incredible connection between horseback riding and animal-assisted therapy, stay tuned for more information in the upcoming article!
Horseback Riding and its Connection to Animal-Assisted Therapy
Horseback riding, a popular recreational activity and sport, is not only enjoyable but also has several benefits for physical, mental, and emotional health. In recent years, the therapeutic potential of horseback riding has been recognized, leading to the emergence of Equine-Assisted Therapy (EAT). EAT combines the power of horses with therapeutic interventions to assist individuals in achieving various physical, emotional, and mental health goals. In this article, we will explore the benefits of horseback riding, different horseback riding techniques, styles, and safety tips. We will also delve into the connection between horseback riding and animal-assisted therapy, its applications, training requirements, and ethical considerations.
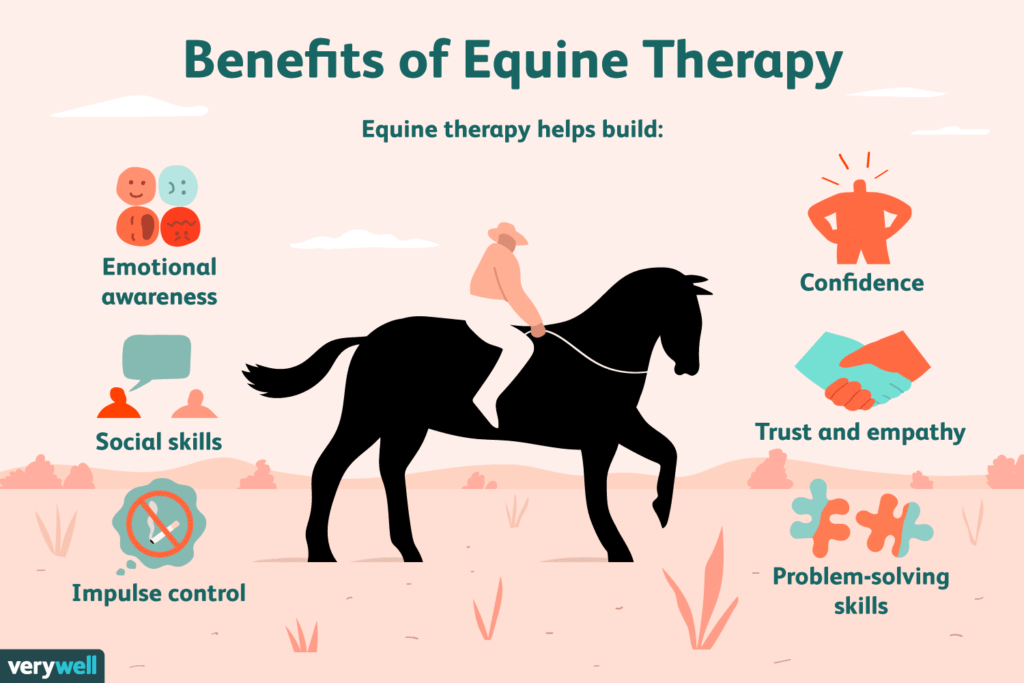
Benefits of Horseback Riding
Physical Health Benefits
Horseback riding is a fantastic form of exercise that offers numerous physical health benefits. As you mount the horse, your muscles naturally engage to maintain balance and control while riding. This activity helps strengthen your core, legs, and back muscles. Additionally, the rhythmic movements of the horse can improve flexibility, coordination, and promote better posture. Regular horseback riding also contributes to cardiovascular fitness and can burn calories, aiding in weight management and overall physical well-being.
Mental Health Benefits
Engaging in horseback riding can have a positive impact on mental health. Being in nature and experiencing the tranquility of horseback riding can reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. The bond and connection formed between the rider and the horse can also boost self-esteem, self-confidence, and improve overall mood. The rhythmic movements of the horse can be calming and provide a sense of relaxation, allowing riders to clear their minds and find mental clarity and peace.
Emotional Benefits
Horseback riding can have profound emotional benefits. The bond created between horse and rider can foster feelings of love, trust, and companionship, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing loneliness or social isolation. The responsibility of taking care of a horse can also enhance feelings of purpose and fulfillment. Interacting with horses and riding can offer a sense of freedom, joy, and a break from the routine of everyday life, positively impacting emotional well-being.
Horseback Riding Techniques
Mounting and Dismounting
Mounting and dismounting a horse correctly is essential for both the rider’s safety and the horse’s well-being. Proper technique involves positioning yourself next to the horse, placing your left foot in the left stirrup, and using your right hand to hold the horse’s reins while placing your left hand on the horse’s withers. With a gentle push off the ground, swing your right leg over the horse’s back and land softly in the saddle. Dismounting is the reverse process, ensuring the rider lands safely on the ground.
Proper Riding Posture
Maintaining proper riding posture is crucial for balance, control, and preventing injuries. You should keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and sit centered in the saddle. Your feet should be placed in the stirrups with heels down, maintaining a slight bend in your knees. Engage your core muscles to maintain stability and alignment. Proper posture will not only ensure an effective and comfortable ride but also allow clear communication with the horse through body language.
Basic Riding Commands
As a rider, you need to learn and understand basic riding commands to communicate effectively with your horse. These commands include using the reins to signal the horse to stop (pull back on the reins), go (apply gentle pressure with your lower legs), turn right or left (apply rein pressure in the desired direction), and back up (apply light backward pressure on the reins). Mastering these commands will help you guide and control the horse safely and efficiently.

Different Styles of Horseback Riding
English Riding
English riding, also known as classical riding, is a style commonly associated with horse shows and equestrian competitions. It focuses on grace, precision, and communication between horse and rider. In English riding, riders use a lightweight saddle and hold the reins with both hands. This style emphasizes a balanced seat, proper posture, and subtle cues to guide the horse.
Western Riding
Western riding is the traditional style associated with cowboys and ranch work. It is known for its distinctive Western saddle and one-handed rein control. Western riding emphasizes a relaxed, deep seat, and riders typically hold the reins in one hand. This style prioritizes comfort, stability, and efficient handling of cattle.
Dressage
Dressage is an intricate style of riding that requires precision and harmony between horse and rider. It involves a series of controlled movements and tests designed to showcase the horse’s training. Dressage focuses on the horse’s suppleness, obedience, and responsiveness to the rider’s aids. Riders use subtle cues from their seat, legs, and reins to communicate with the horse.
Safety Tips for Horseback Riding
Wearing Protective Gear
When horseback riding, it is crucial to prioritize safety by wearing appropriate protective gear. A well-fitting riding helmet is essential to protect your head from potential injuries in case of a fall or accident. Additionally, wearing sturdy boots with a heel can prevent your foot from slipping through the stirrup, reducing the risk of getting dragged or trapped if you fall. It is also advisable to wear long pants and gloves to provide protection and enhance grip.
Choosing the Right Horse
Selecting the right horse for your riding ability is paramount to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience. If you are a beginner or novice rider, opt for a well-trained, calm, and patient horse. Horses with a good temperament and experience working with riders of different levels will provide a more pleasant and confidence-building experience. It is also essential to match the horse’s size and physical capabilities to your own.
Checking Equipment
Before each ride, it is crucial to check your riding equipment, including the saddle, bridle, reins, and girth. Ensure that the saddle is secure and fits the horse properly, without any loose or damaged parts. Check the bridle for any cracked or worn-out leather and make sure the reins are intact. The girth should be tightened appropriately but not too tightly, to avoid discomfort for the horse. Regular equipment maintenance and inspection are vital for your safety and the horse’s well-being.

Horse Care and Maintenance
Feeding and Nutrition
Proper feeding and nutrition are paramount to ensure the health and well-being of horses. Horses should have access to fresh, clean water at all times. Their diet should consist of high-quality forage, such as hay or pasture, which provides essential nutrients and aids in digestion. Depending on their breed, age, and activity level, horses may also require additional concentrates, such as grains or specialized feeds. It is important to consult with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to develop an appropriate feeding plan for your horse.
Grooming and Hygiene
Regular grooming is essential for maintaining a horse’s health and well-being. Grooming includes brushing the horse’s coat to remove dirt, debris, and loose hair, which helps promote good circulation and a healthy coat. It also involves cleaning the hooves, checking for any abnormalities or signs of infection. Additionally, grooming provides an opportunity to bond with the horse and monitor their overall condition.
Stable Management
Proper stable management is crucial for the comfort and safety of horses. Stables should be well-ventilated, clean, and free from hazards. Regular stall cleaning, including removing manure and replenishing bedding, ensures a clean living environment for the horse. Adequate turnout and exercise are also important to prevent boredom and promote physical and mental well-being. Regular veterinary care, vaccinations, and preventive measures for parasites are vital components of stable management.
Understanding Horses and Their Behavior
Horse Communication
Horses communicate primarily through body language, using a complex system of gestures, movements, and vocalizations. Understanding their communication cues can help riders and handlers build a stronger bond and ensure effective interaction. Horses use their ears, eyes, tail, and body position to convey various messages, such as relaxation, discomfort, curiosity, or aggression. Observing and interpreting these signs can enhance your ability to respond appropriately to the horse’s needs and emotions.
Horse Body Language
A horse’s body language provides valuable insight into its emotions and intentions. Ears positioned forward indicate attentiveness and curiosity, while pinned-back ears can indicate aggression or discomfort. Relaxed and loose movements of the tail and body signify contentment, while tense muscles and tail swishing may signal unease or agitation. Understanding and interpreting these subtle cues can help establish a positive and trusting relationship with the horse.
Building Trust with Horses
Building trust with a horse is essential for effective riding and handling. Trust is established through consistent, patient, and gentle interactions. Developing a routine and providing positive reinforcement, such as treats or praise, can help foster trust. Spending time bonding, grooming, and engaging in activities that the horse enjoys will strengthen the bond and build confidence. Respect the horse’s boundaries and always prioritize their well-being to establish a foundation of trust.

Equine-Assisted Therapy
What is Equine-Assisted Therapy?
Equine-Assisted Therapy (EAT) is a form of therapeutic intervention that utilizes horses to address various physical, emotional, and mental health conditions. It is conducted under the guidance of qualified therapists and equine professionals. EAT involves engaging with horses in various activities, such as riding, grooming, and groundwork, to achieve specific therapeutic goals. The presence of the horse and the unique bond formed with the client can facilitate emotional and psychological growth.
Benefits of Equine-Assisted Therapy
Equine-Assisted Therapy offers a wide range of benefits for individuals of all ages and abilities. It can aid in improving physical strength, balance, coordination, and motor skills. EAT has shown significant positive effects on individuals with mental health conditions, including reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The emotional connection and trust formed between the client and the horse can enhance self-esteem, self-confidence, and social skills.
Different Approaches to Equine-Assisted Therapy
Equine-Assisted Therapy encompasses various approaches, depending on the specific goals and needs of the client. Therapeutic horseback riding focuses on the physical benefits of riding and can aid in improving muscle strength, coordination, and balance. Equine-facilitated psychotherapy involves non-riding activities, such as grooming, leading, and observing horses, to promote emotional growth and mental well-being. Other approaches include hippotherapy, which utilizes the horse’s movement for physical therapy, and therapeutic vaulting, which combines gymnastics and horseback riding for therapeutic purposes.
Animal-Assisted Therapy vs. Traditional Therapy
Differences and Similarities
Animal-Assisted Therapy (AAT) and traditional therapy have several key differences and similarities. Traditional therapy involves a therapist or counselor working directly with a client, using various therapeutic techniques and interventions to achieve specific treatment goals. AAT, on the other hand, integrates animals, such as horses, dogs, or cats, into the therapeutic process. Both approaches aim to improve clients’ mental health and well-being but utilize different strategies and modalities.
One significant difference is the presence of animals in AAT, which can enhance the therapeutic experience and create unique opportunities for connection and emotional healing. Animals provide unconditional love, support, and non-judgmental companionship, creating a safe and nurturing environment for the client. Traditional therapy primarily focuses on verbal communication and relies on the therapist-client relationship to facilitate change and personal growth.
Effectiveness of Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animal-Assisted Therapy has shown promising results in improving various mental health conditions and enhancing overall well-being. Interacting with animals can release endorphins, reduce stress, and lower blood pressure and heart rate. The presence of animals can also increase feelings of trust, security, and comfort, helping individuals open up and engage more effectively in the therapeutic process. Animal-Assisted Therapy has been particularly effective in treating individuals with PTSD, anxiety disorders, autism spectrum disorder, and depression.
Combining Animal-Assisted Therapy with Traditional Therapy
Combining Animal-Assisted Therapy with traditional therapy approaches can offer a comprehensive and multi-modal treatment option. Traditional therapy provides a framework for addressing specific psychological concerns, while animal interaction enhances the therapeutic experience, deepens the client’s emotional connection, and promotes overall well-being. Animal-Assisted Therapy can complement traditional therapy by providing a unique avenue for self-expression, self-discovery, and personal growth.

Applications of Horseback Riding in Animal-Assisted Therapy
Physical Rehabilitation
Horseback riding can be a valuable tool in physical rehabilitation due to the horse’s rhythmic movements. The three-dimensional motion of the horse’s gait stimulates the rider’s muscles, joints, and vestibular system, promoting balance, coordination, and strengthening core muscles. Horseback riding also encourages increased range of motion, improved posture, and can be an effective form of cardiovascular exercise for individuals with physical disabilities.
Emotional and Mental Health Treatment
Horseback riding in the context of Animal-Assisted Therapy can be a powerful intervention for individuals with emotional and mental health conditions. The relationship formed between the rider and the horse can provide a sense of emotional security, trust, and acceptance. Riding can help individuals develop coping mechanisms, manage stress and anxiety, and improve emotional regulation. The opportunity for non-verbal communication with the horse can also be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle with expressing their emotions verbally.
Special Needs Education
Horseback riding is often utilized in special needs education as it offers unique benefits for individuals with physical, cognitive, and emotional disabilities. Therapeutic horseback riding programs can help individuals with autism spectrum disorder, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, and other developmental conditions improve their balance, motor skills, and overall physical well-being. Riding can also foster social interaction, self-confidence, and provide a sense of achievement and empowerment.
Training and Certification for Equine-Assisted Therapy
Requirements for Equine-Assisted Therapy Practitioners
Practitioners involved in Equine-Assisted Therapy must meet specific requirements to ensure the safety and effectiveness of therapeutic sessions. The qualifications vary depending on the specific country, region, or organization providing the therapy. Generally, practitioners should have a relevant educational background in fields such as psychology, counseling, social work, or occupational therapy. Additional certifications in Equine-Assisted Therapy or related disciplines are often required. Equine knowledge and experience, including horsemanship and handling skills, are also essential for practitioners involved in horseback riding-based therapies.
Training Programs and Courses
Various training programs and courses are available to individuals interested in becoming Equine-Assisted Therapy practitioners. These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of the therapeutic principles, horse behavior, and practical skills required for conducting successful therapy sessions. Training programs typically cover topics such as the ethics of Equine-Assisted Therapy, horse anatomy and health, groundwork, and riding techniques in a therapeutic context. It is important to select an accredited training program or course to ensure high-quality education and adherence to professional standards.
Certification and Accreditation
Certification and accreditation provide a level of professional recognition and ensure the practitioners meet specific standards of competence and ethical conduct. Certification processes vary depending on the region and organization. Typically, practitioners need to complete the required training, gain practical experience, and pass the certification examination. Accreditation of the therapy facility or organization may also be necessary, ensuring adherence to safety protocols, animal welfare standards, and ethical practices.
Research and Evidence Supporting Horseback Riding in Therapy
Scientific Studies on the Impact of Horseback Riding on Mental Health
Scientific studies have demonstrated the positive impact of horseback riding as a therapeutic intervention for mental health conditions. Research has shown that horseback riding can reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and improve overall well-being. Studies have also found that horseback riding interventions can enhance social skills, communication, and emotional regulation, particularly in children and adolescents. The rhythmic movements and the bond formed with the horse can release endorphins, reduce stress, and promote a sense of calm and relaxation.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous case studies and success stories highlight the transformative power of horseback riding in therapy. These stories illustrate the positive impact that riding can have on individuals with a multitude of physical, emotional, and mental health challenges. From individuals with PTSD finding solace and healing through horseback riding to children with autism spectrum disorder improving their communication and social skills, the anecdotal evidence showcases the profound impact that horses can have on human well-being.
Professional Recommendations
Professional organizations, such as the American Hippotherapy Association and the Professional Association of Therapeutic Horsemanship International (PATH Intl.), provide recommendations and guidelines for incorporating horseback riding in therapy. These organizations promote evidence-based practice and emphasize the importance of qualified practitioners, well-trained horses, and safe environments for therapeutic riding. They provide resources, workshops, and conferences to support ongoing professional development and encourage best practices.
Ethical Considerations in Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animal Welfare and Safety
Ethical considerations in Animal-Assisted Therapy revolve around ensuring animal welfare and safety. Practitioners must prioritize the well-being of the animals involved, providing appropriate care, nutrition, and living conditions. Animals should undergo regular veterinary check-ups and receive necessary vaccinations and preventive treatments. It is essential to monitor their behavior, prevent overworking or stressing the animals, and provide them with opportunities for rest and social interaction.
Informed Consent and Confidentiality
Obtaining informed consent and ensuring client confidentiality are crucial ethical considerations in therapy. Before commencing therapy, clients should be fully informed about the goals, potential risks, and benefits of the therapy involving animals. Consent should be voluntary, and clients need to have the option to withdraw from therapy at any time. Practitioners are also responsible for maintaining client confidentiality, safeguarding their personal and sensitive information, and adhering to legal and ethical confidentiality standards.
Boundaries and Professional Ethics
Maintaining clear boundaries and upholding professional ethics are essential aspects of Animal-Assisted Therapy. Practitioners must establish and communicate clear professional boundaries with clients, ensuring an appropriate therapeutic relationship. They must avoid dual relationships or conflicts of interest that could compromise objectivity and professional judgment. Ethical guidelines also include respecting cultural and individual differences, maintaining competence through ongoing education, and engaging in professional supervision and consultation.
Legislation and Regulations for Equine-Assisted Therapy
Legal Responsibilities
Equine-Assisted Therapy is subject to various legislation and regulations to ensure safety, animal welfare, and the ethical practice of therapy. The specific legal responsibilities vary depending on the country or region. Practitioners and therapy facilities must comply with relevant animal welfare acts, disability rights acts, and health and safety regulations. They may also need to adhere to professional licensing and insurance requirements to protect both clients and practitioners.
Licensing and Permits
Licensing and permit requirements for Equine-Assisted Therapy depend on the specific country or region. These regulations aim to ensure that therapy providers meet minimum standards of competence, animal welfare, and safety. Licensing or permit processes may involve inspections of therapy facilities, certification of practitioners, and compliance with specific guidelines and protocols. Licensing and permits also demonstrate accountability and provide reassurance to clients and referring professionals.
Insurance Requirements
Equine-Assisted Therapy practitioners and therapy facilities should have appropriate insurance coverage to protect against potential risks and liabilities. Insurance requirements may include general liability coverage, professional liability insurance, and worker’s compensation. Insurance coverage ensures financial protection for both the client and the therapy providers in the event of accidents, injuries, or other unforeseen circumstances.
Conclusion
Horseback riding is not just a recreational activity but also a valuable therapeutic tool. The physical, mental, and emotional benefits of horseback riding have led to the emergence of Equine-Assisted Therapy, which utilizes horses to assist individuals in achieving their health and well-being goals. Horseback riding promotes physical strength, coordination, and cardiovascular fitness while also providing a source of relaxation, stress relief, and emotional connection. In the context of Animal-Assisted Therapy, horseback riding has shown remarkable results in treating a wide range of physical, emotional, and mental health conditions. It is crucial for practitioners to have the necessary qualifications, training, and understanding of animal welfare and ethics to provide safe and effective therapy. As horseback riding continues to gain recognition as a therapeutic intervention, further research and evidence will continue to support its efficacy and broaden its applications in the field of animal-assisted therapy.
